Artificial intelligence (AI) has compelled its method into the public consciousness because of the introduction of highly effective new AI chatbots and picture mills. However the subject has a protracted history stretching again to the dawn of computing. Given how basic AI may very well be in altering how we dwell in the coming years, understanding the roots of this fast-developing subject is essential. Listed here are 12 of the most essential milestones in the history of AI.
1950 — Alan Turing’s seminal AI paper

Famend British pc scientist Alan Turing printed a paper titled “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” which was one of the first detailed investigations of the query “Can machines suppose?”.
Answering this query requires you to first sort out the problem of defining “machine” and “suppose.” So, as an alternative, he proposed a recreation: An observer would watch a dialog between a machine and a human and attempt to decide which was which. In the event that they could not accomplish that reliably, the machine would win the recreation. Whereas this did not show a machine was “pondering,” the Turing Check — because it got here to be identified — has been an essential yardstick for AI progress ever since.
1956 — The Dartmouth workshop

AI as a scientific self-discipline can hint its roots again to the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence, held at Dartmouth Faculty in 1956. The contributors have been a who’s who of influential pc scientists, together with John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky and Claude Shannon. This was the first time the time period “synthetic intelligence” was used as the group spent nearly two months discussing how machines would possibly simulate studying and intelligence. The assembly kick-started critical analysis on AI and laid the groundwork for a lot of of the breakthroughs that got here in the following a long time.
1966 — First AI chatbot
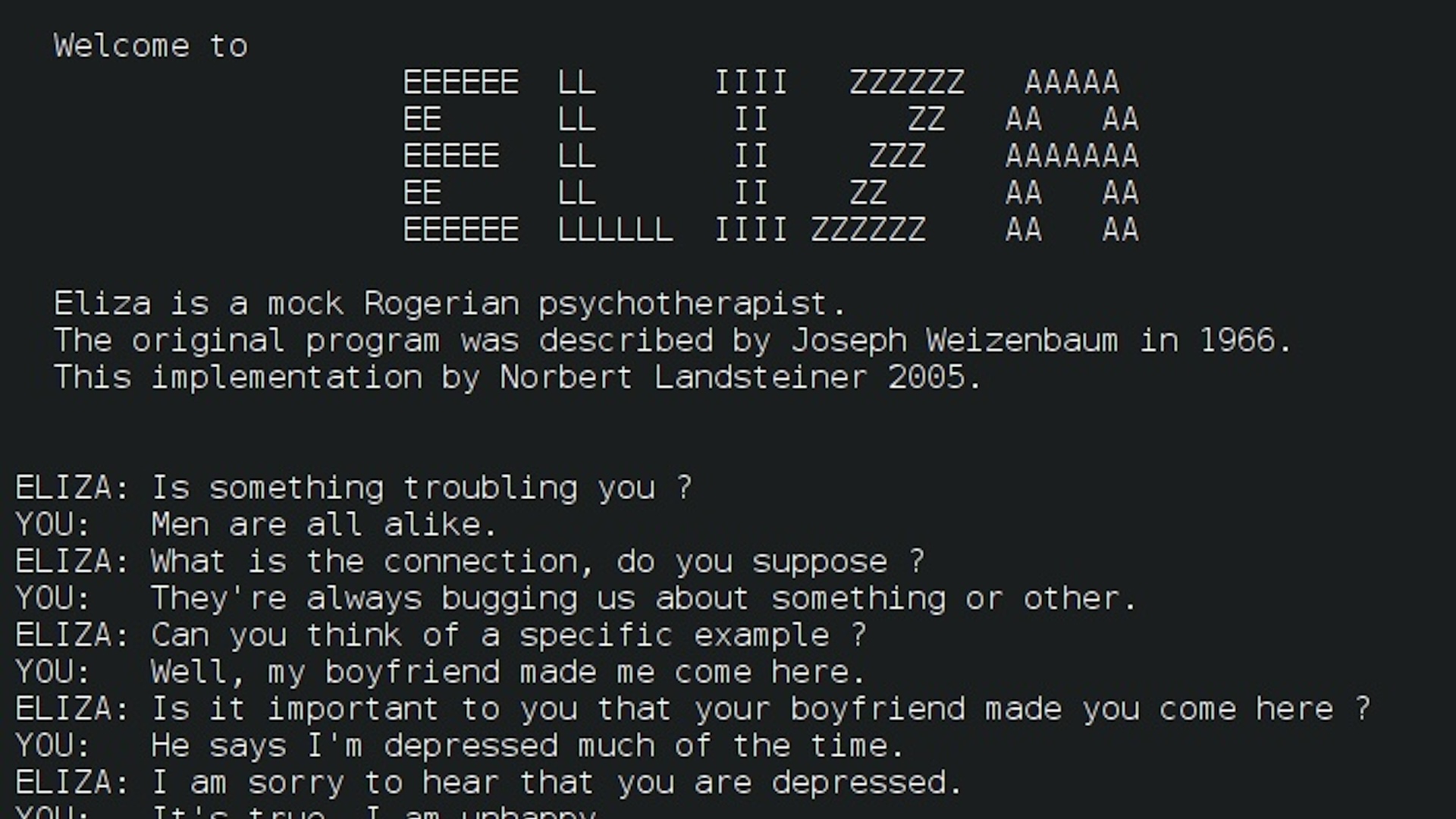
MIT researcher Joseph Weizenbaum unveiled the first-ever AI chatbot, generally known as ELIZA. The underlying software program was rudimentary and regurgitated canned responses based mostly on the key phrases it detected in the immediate. Nonetheless, when Weizenbaum programmed ELIZA to behave as a psychotherapist, individuals have been reportedly amazed at how convincing the conversations have been. The work stimulated rising interest in natural language processing, together with from the U.S. Protection Superior Analysis Tasks Company (DARPA), which supplied appreciable funding for early AI analysis.
1974-1980 — First “AI winter”
It did not take lengthy earlier than early enthusiasm for AI started to fade. The Nineteen Fifties and Nineteen Sixties had been a fertile time for the subject, however in their enthusiasm, main specialists made daring claims about what machines can be succesful of doing in the close to future. The know-how’s failure to dwell as much as these expectations led to rising discontent. A highly critical report on the subject by British mathematician James Lighthill led the U.Okay. authorities to chop nearly all funding for AI analysis. DARPA additionally drastically reduce funding round this time, resulting in what would turn into generally known as the first “AI winter.”
1980 — Flurry of “knowledgeable methods”

Regardless of disillusionment with AI in many quarters, analysis continued — and by the begin of the Eighties, the know-how was beginning to catch the eye of the personal sector. In 1980, researchers at Carnegie Mellon College constructed an AI system called R1 for the Digital Tools Company. This system was an “knowledgeable system” — an strategy to AI that researchers had been experimenting with since the Nineteen Sixties. These methods used logical guidelines to cause via massive databases of specialist information. This system saved the firm hundreds of thousands of {dollars} a 12 months and kicked off a increase in trade deployments of knowledgeable methods.
1986 — Foundations of deep studying

Most analysis so far had targeted on “symbolic” AI, which relied on handcrafted logic and information databases. However since the start of the subject, there was additionally a rival stream of analysis into “connectionist” approaches that have been impressed by the mind. This had continued quietly in the background and eventually got here to mild in the Eighties. Fairly than programming methods by hand, these methods concerned coaxing “synthetic neural networks” to be taught guidelines by coaching on information. In idea, this could result in extra versatile AI not constrained by the maker’s preconceptions, however coaching neural networks proved difficult. In 1986, Geoffrey Hinton, who would later be dubbed one of the “godfathers of deep studying,” printed a paper popularizing “backpropagation” — the coaching approach underpinning most AI methods as we speak.
1987-1993 — Second AI winter

Following their experiences in the Seventies, Minsky and fellow AI researcher Roger Schank warned that AI hype had reached unsustainable ranges and the subject was in hazard of one other retraction. They coined the time period “AI winter” in a panel discussion at the 1984 assembly of the Affiliation for the Development of Synthetic Intelligence. Their warning proved prescient, and by the late Eighties, the limitations of knowledgeable methods and their specialised AI {hardware} had began to turn into obvious. Business spending on AI lowered dramatically, and most fledgling AI corporations went bust.
1997 — Deep Blue’s defeat of Garry Kasparov
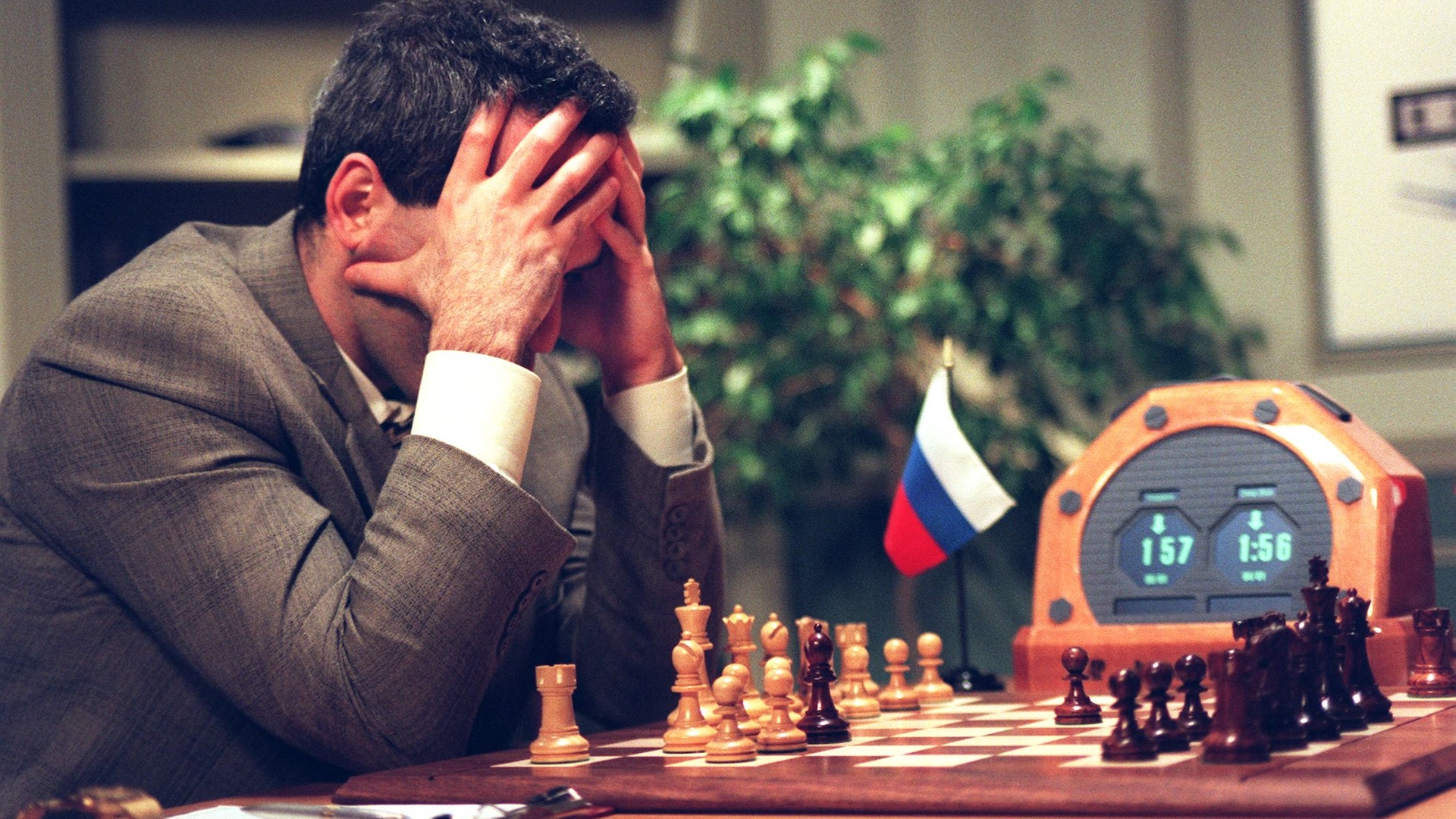

Regardless of repeated booms and busts, AI analysis made regular progress throughout the Nineteen Nineties largely out of the public eye. That modified in 1997, when Deep Blue — an knowledgeable system constructed by IBM — beat chess world champion Garry Kasparov in a six-game series. Aptitude in the complicated recreation had lengthy been seen by AI researchers as a key marker of progress. Defeating the world’s greatest human participant, due to this fact, was seen as a serious milestone and made headlines round the world.
2012 — AlexNet ushers in the deep studying period

Regardless of a wealthy physique of educational work, neural networks have been seen as impractical for real-world functions. To be helpful, they wanted to have many layers of neurons, however implementing massive networks on standard pc {hardware} was prohibitively inefficient. In 2012, Alex Krizhevsky, a doctoral pupil of Hinton, gained the ImageNet pc imaginative and prescient competitors by a big margin with a deep-learning mannequin known as AlexNet. The key was to make use of specialised chips known as graphics processing items (GPUs) that might effectively run a lot deeper networks. This set the stage for the deep-learning revolution that has powered most AI advances ever since.
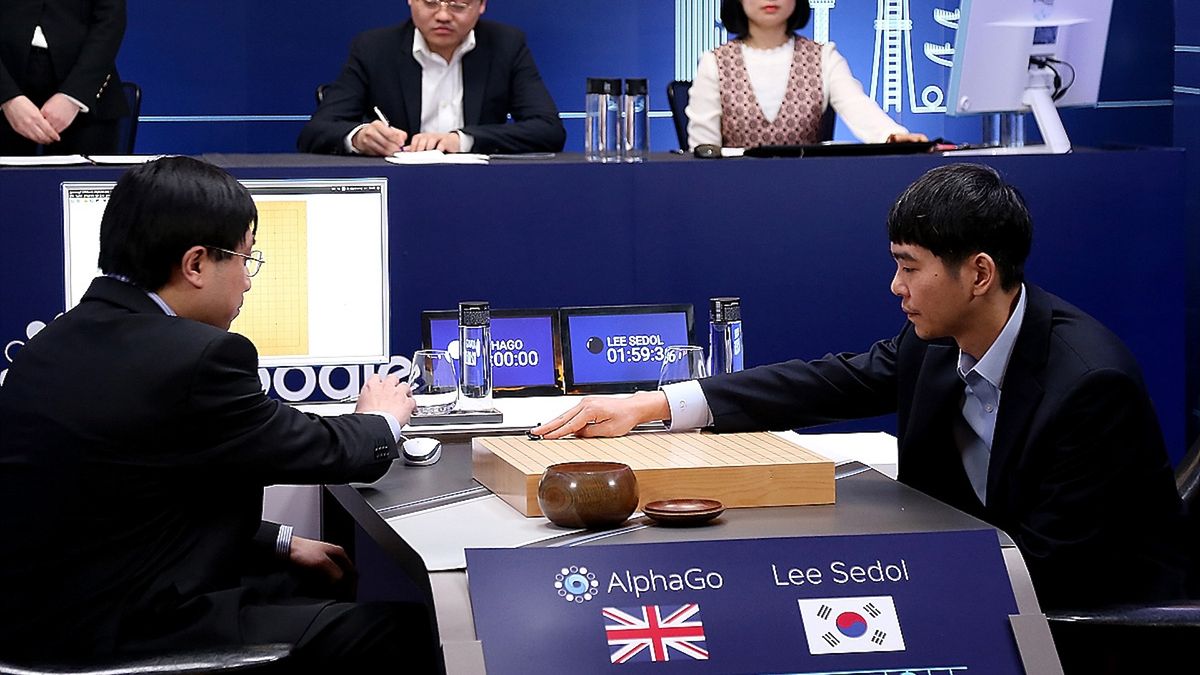
2016 — AlphaGo’s defeat of Lee Sedol
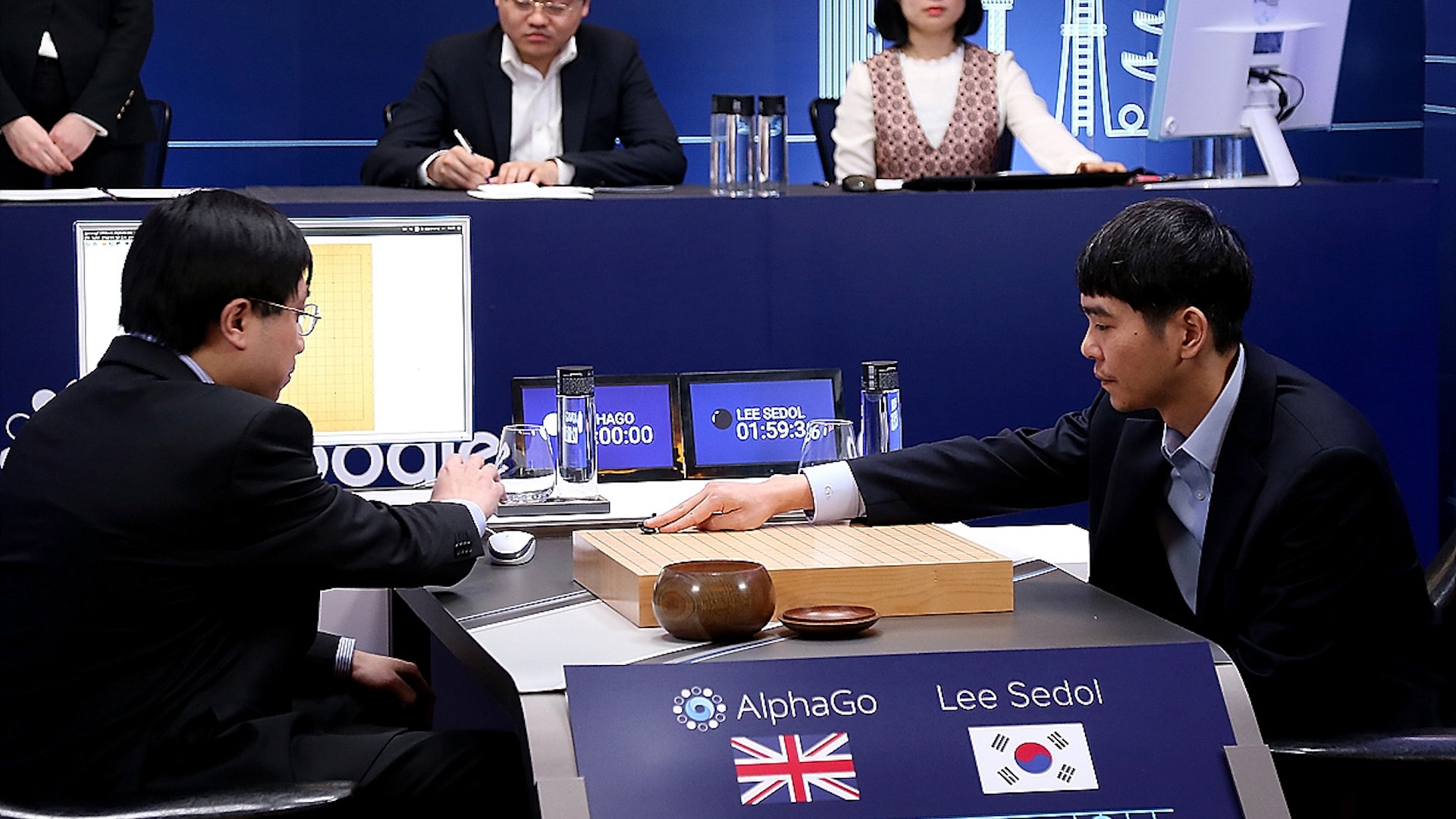

Whereas AI had already left chess in its rearview mirror, the rather more complicated Chinese language board recreation Go had remained a problem. However in 2016, Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo beat Lee Sedol, one of the world’s best Go gamers, over a five-game sequence. Consultants had assumed such a feat was nonetheless years away, so the consequence led to rising pleasure round AI’s progress. This was partly attributable to the general-purpose nature of the algorithms underlying AlphaGo, which relied on an strategy known as “reinforcement studying.” On this approach,AI methods successfully be taught via trial and error. DeepMind later prolonged and improved the strategy to create AlphaZero, which may educate itself to play all kinds of video games.
2017 — Invention of the transformer structure

Regardless of important progress in pc imaginative and prescient and recreation taking part in, deep studying was making slower progress with language duties. Then, in 2017, Google researchers printed a novel neural community structure known as a “transformer,” which might ingest huge quantities of information and make connections between distant information factors. This proved notably helpful for the complicated process of language modeling and made it doable to create AIs that might concurrently sort out a range of duties, comparable to translation, textual content era and doc summarization. All of as we speak’s main AI fashions depend on this structure, together with picture mills like OpenAI’s DALL-E, in addition to Google DeepMind’s revolutionary protein folding mannequin AlphaFold 2.
2022 – Launch of ChatGPT

On Nov. 30, 2022, OpenAI launched a chatbot powered by its GPT-3 massive language mannequin. Generally known as “ChatGPT,” the device grew to become a worldwide sensation, garnering greater than 1,000,000 customers in lower than every week and 100 million by the following month. It was the first time members of the public might work together with the newest AI fashions — and most have been blown away. The service is credited with beginning an AI increase that has seen billions of {dollars} invested in the subject and spawned quite a few copycats from massive tech corporations and startups. It has additionally led to rising unease about the tempo of AI progress, prompting an open letter from distinguished tech leaders calling for a pause in AI analysis to permit time to evaluate the implications of the know-how.
