Online political participation of college college students
Political participation refers to the habits of residents who participate in the political course of and have the intention or precise impact of influencing the federal government’s motion [19]. With the event of the Web and new media, the residents’ political participation habits has been expanded from offline to online [20], and has developed from the normal types of offline rallies and marches to the handy and quick completion of the participation habits with the assistance of the Web platform. Subsequently, residents’ makes an attempt to affect the political course of by partaking in online platforms are referred to as online political participation. Online political participation is a crucial ingredient in the examine of political participation.
With the event of Web expertise, the scope of online political participation has turn out to be broader and broader, together with signing or sharing online petitions, collaborating in online opinion polls, and so forth. Some students additionally imagine that the dialogue of political points and content material dissemination in our on-line world belong to the content material of online political participation as effectively [21,22,23,24]. In contrast with different youth teams, college college students are extra lively in paying consideration to info, expressing their opinions, and utilizing the Web extra ceaselessly, due to this fact, online political participation of college college students is undoubtedly an necessary subject in the digital age, and a analysis discipline to which college college students at house and overseas pay a lot consideration in phrases of political participation on the college stage.
Some research have identified that college college students have shifted from the normal “dutiful citizenship” fashion of political participation to a “actual citizenship” fashion, in which they categorical their political positions in their every day lives by liking, forwarding and commenting on the Web, a type of participation that researchers refer to as “latent political participation” [3, 25], which is believed could possibly be free from the constraints of time and financial prices, and in addition the commonest type of online political participation among the many college scholar inhabitants.
Impression of artificial intelligence on college college students’ online political participation
For fairly a very long time, the political participation habits of Chinese youth teams has been primarily primarily based on the decision for participation by the federal government and colleges [26, 27].With the event of social media and AI, its low-threshold, omni-directional, and all-time-space traits enable youth teams to entry an increasing number of political info, and as such the social media platforms have progressively turn out to be an necessary channel for the youths to convey their political beliefs [28]. Analysis has discovered that people’ entry to online info enriches their political data and stimulates political enthusiasm, thus affecting online political participation positively [29, 30]. Subsequently, with the development of AI expertise, present Chinese college college students are progressively altering from passive members in political participation to lively members in public affairs and lively boosters of online public opinions [31].
Artificial intelligence expertise reduces the time value and financial value of college college students’ entry to info, and in addition improves the effectivity of info dissemination [32]. The existence of AI has led to an exponential development in the amount, dissemination vary and pace of political info, and so forth. Beneath the affect of AI expertise, college college students can not solely actively search to receive political info, but in addition passively obtain scorching information info by way of the existence of large information and algorithmic advice expertise. The rise in the frequency and amount of political info reception expands their alternatives to study public affairs, which influences their willingness to participate in politics [5, 33] and stimulates them to produce political participation behaviours [34].
Then again, AI can even have unfavourable impacts on college college students’ online political participation equivalent to interference and misinformation. Deep mining of college college students’ looking habits and data wants and focused info pushing may also help obtain a exact allocation between info manufacturing and particular person wants [16], however it could actually additionally make college college students make irrational selections by reinforcing a sure single political viewpoint due to the affect of the “info cocoon” impact, or lead to retreat and avoidance behaviours [17]. On the similar time, deep falsification expertise can produce false info equivalent to voice cloning, picture synthesis, video synthesis, and so forth., which is able to lead to cognitive bias amongst college college students, weakening the credibility of political info to a sure extent, thus affecting the willingness to participate and decision-making outcomes.
On this examine, online political participation of college college students in the context of AI is outlined because the behaviour of college college students who use clever and personalised instruments and platforms supplied by AI expertise to participate in and affect the political decision-making course of in a direct or oblique means.
Artificial intelligence can even have an effect on college college students’ online participation behaviour by influencing their sense of political efficacy. Political efficacy is an attitudinal variable that impacts residents‘ political participation, referring to residents’ notion and analysis of the affect their participation in politics can have in the political course of [35], and is the motivational issue behind political participation behaviour [36]. Political efficacy is categorised into inside and exterior efficacy, with inside efficacy referring to a person’s notion of his or her skill to affect authorities and political selections, and exterior efficacy referring to a person’s notion of the state of governmental responsiveness, reflecting a person’s skill to participate in political actions and the concepts held in regards to the effectiveness of participation [37, 38]. Research have recommended that the extent of political efficacy is a big predictor of a person’s political participation behaviour, and that individuals with a excessive stage of political efficacy might be extra inclined to participate in public affairs [39] and also will be extra lively in the participation course of [40, 41], equivalent to being extra concerned when voting [42]. In distinction, folks with low political efficacy have a tendency to present extra political apathy and withdrawal tendencies. By analysing the voting information through the US election, some research have discovered that online political discussions assist to enhance residents‘ sense of political participation efficacy [43], and that political info posted and shared by shut associates on the Web al.so has a direct affect on residents’ political attitudes and voting behaviour.
The event of digital expertise has enabled the media to play an more and more position of significance in the political perceptions of college college students. Some students have argued that residents can enhance their confidence in political participation by studying about information experiences or the experiences of others [36, 44,45,46], and in addition by weakening the strain of social norms on the political participation behaviors of college scholar teams [47], permitting them to categorical their views extra freely and overtly [48, 49], stimulating college college students to develop a stronger curiosity in political participation [50], and rising their involvement in political actions [51, 52], to understand their calls for.
Idea of deliberate habits
Of the prevailing fashions used to perceive and predict human habits, the Idea of Deliberate Conduct (TPB) is essentially the most influential and extensively acknowledged and used in research, which is proposed by psychologist Ajzen [53]. And such TPB measures particular person cognition from three dimensions: particular person angle in the direction of habits, subjective norms, and perceptual behavioral management, and argues that a person’s stage of cognition determines the willingness to act, which in flip influences his or her behavioral decision-making [53], i.e., the extra optimistic a person’s angle is, the larger his or her sense of norms is, and the decrease the diploma of perceived issue, the stronger his or her willingness to act. The extra optimistic a person’s angle is and the much less issue he or she perceives, the stronger his or her willingness might be and the upper the chance that he or she’s going to commit a specific habits. Thus, college college students’ willingness to participate in online political actions refers to their psychological expectation or subjective need to participate in online political actions, which is the “prelude” to their eventual adoption of online political participation behaviors. Moreover, primarily based on this TPB mannequin, college college students’ behavioral attitudes, subjective norms and perceived behavioral management of online political participation will have an effect on their willingness to participate, and thus have an effect on their online political participation behaviors.
Moreover, as described in such TPB mannequin, behavioral angle refers to the person’s analysis of his/her liking or disliking of the participation habits, together with the worth judgement of the habits and the evaluation of the results, and a few research have proved that the extra optimistic the person’s behavioral angle is, the stronger his/her willingness to participate might be [54]. It has been discovered that college college students’ mastery of political info impacts their willingness to participate, and their political curiosity, political belief, notion of the associated fee of the habits, and expectation of the impact of the habits additionally have an effect on their political notion and willingness to participate [55]. Apart from, the values and political psychological elements can also have a larger affect on online political participation [56, 57].
Subjective norms refer to a person’s perceived strain to carry out or not carry out a sure habits, which primarily originates from socially shut important others or teams [53]. Subjective norms of college college students’ online political participation refer to the social strain and subjective affect of important others round college college students on whether or not they participate in online political habits, which for college college students primarily embody relations, classmates, academics, and members of online teams. College college students are extra possible to interact in online political behaviors if they’re perceived as essential by their important others, particularly members of their online group. Then, the subjective norms have a direct affect on college college students’ online political participation habits.
Perceived behavioral management signifies a person’s confidence in his or her skill to carry out a habits efficiently, and this notion is especially derived from circumstances that facilitate or hinder the manufacturing of the habits. Thus, this perceived behavioral management is reported to be measured by way of self-efficacy and perceived limitations [58, 59]. College college students’ skill to interact in online political participation is carefully associated to their every day experiences and their private traits, and the diploma of issue in collaborating and their notion of the end result of participation are necessary facets that have an effect on their participation habits. In different phrases, the stronger the online behavioral skill of college college students, the stronger their willingness to participate, and the much less they’re hindered by exterior obstacles, the stronger their willingness to participate.
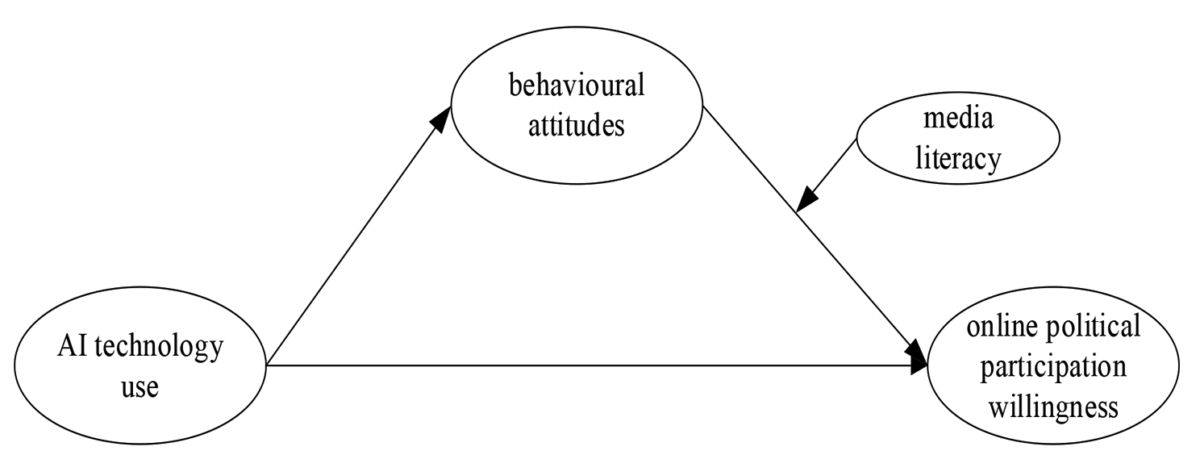
Accordingly, the next three hypotheses are proposed with the analysis mannequin as schemed in Fig. 1.
H1
Artificial intelligence use positively predicts college college students’ online political participation willingness.
H2a
Behavioural attitudes of college college students mediate the connection between AI use and willingness to participate in online politics.
H2b
College college students’ subjective norms mediate the connection between AI use and online political participation intentions.
H2c
College college students’ perceived behavioural management mediates the connection between AI use and willingness to participate in online politics.
H3a
Media literacy stage moderates the connection between college college students’ behavioural attitudes and willingness to interact in online political participation.
H3b
Stage of media literacy moderates the connection between college college students’ subjective norms and willingness to interact in online political participation.
H3c
Media literacy stage moderates the connection between perceived behavioural management and willingness to participate in online politics amongst college college students.