Healthcare informatician—respondent traits
Of 101 respondents to the healthcare informatician survey, a majority have been higher than 40 years outdated (54.5%), male (62.0%), and white (70.1%) (Desk 1). Respondents might establish as a couple of function; most have been clinicians (44.6%), adopted by information scientists (36.6%). Most respondents reported that they’d been working towards in informatics for greater than 10 years (54.5%).
Most felt they have been very effectively knowledgeable (41.6%) or sufficiently knowledgeable (48.5%) about AI/ML, with a majority reporting that they’d taken coursework on the subject (61.4%) or have been doing analysis on the subject (68.3%). A big portion additionally reported that they’d labored on deploying AI/ML (42.6%).
Clinician survey—respondent traits
Of 607 US-based respondents to the clinician survey, a majority have been 40 years outdated or youthful (69.9%), feminine (55.7%), and white (68.2%) (Desk 2). Physicians made up 70.7% of respondents, of which 45.4% have been trainees. Hospital drugs was the commonest specialty (52.1%) adopted by hematology (20.8%). A majority of respondents (65.8%) reported making a choice about whether or not a affected person wants VTE prophylaxis day by day. Solely 20.5% of respondents reported that they’d used AI/ML to tell their medical follow; a majority had not (57.9%) or have been not sure (21.6%).
Healthcare informatician—experiences with AI/ML
Most informaticians (62.6%) reported that their group is utilizing or growing AI/ML for healthcare. Of those 62 respondents, a majority described the standing of AI/ML at their group as carried out with not less than one mannequin in use (82.3%), and that their organizations primarily develop the fashions themselves (81.4%). Lower than half (45.8%) reported utilizing third-party distributors or partnering with native universities (28.8%).
Respondents who reported growing AI/ML programs used Python (76.6%), R (45.3%), and toolkits (42.2%). Of the respondents who described what toolkit they like, probably the most generally cited ones have been Scikit-learn and TensorFlow.
Healthcare informatician—attitudes in direction of AI/ML
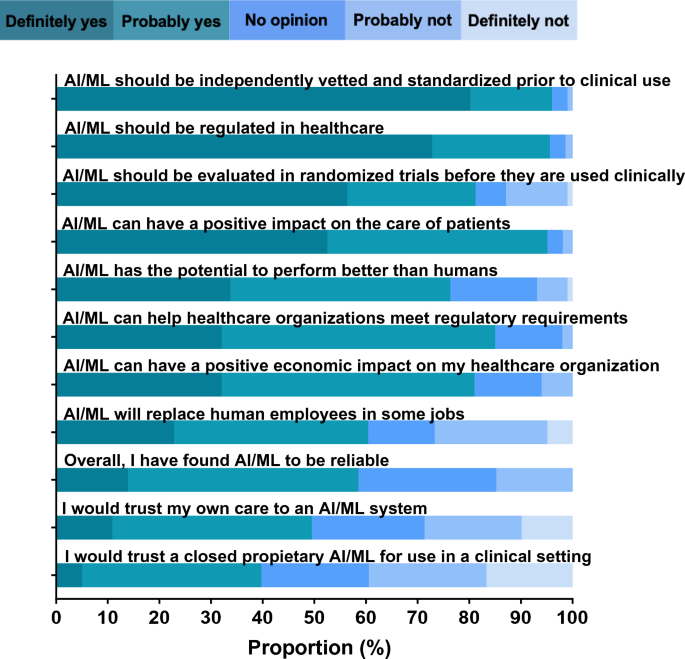
A majority of informaticians agreed that AI/ML can have a optimistic affect on the care of sufferers (95.0%), may help healthcare organizations meet regulatory necessities (95.0%), and can have a optimistic financial affect on their healthcare group (81.0%) (Fig. 1, Supplementary Desk 1). Informaticians principally agreed that AI/ML has the potential to carry out higher than people (76.3%) and will change human staff in some jobs (60.4%). Respondents discovered AI/ML to be total dependable (58.5%) and would belief their very own care to an AI/ML system (49.5%). Nonetheless, lower than half would belief a closed proprietary system (39.7%). Most informaticians agreed that AI/ML needs to be independently vetted and standardized previous to use in a medical setting (96.0%), regulated (95.6%), and evaluated in randomized managed trials (81.2%).
The three commonest causes respondents recognized as limitations to the profitable improvement of AI/ML in healthcare have been information high quality (67.3%), lack of standardization (39.8%), and problem of acceptance by healthcare suppliers (35.7%).
Healthcare informatician—attitudes in direction of AI/ML for the administration of blood clots
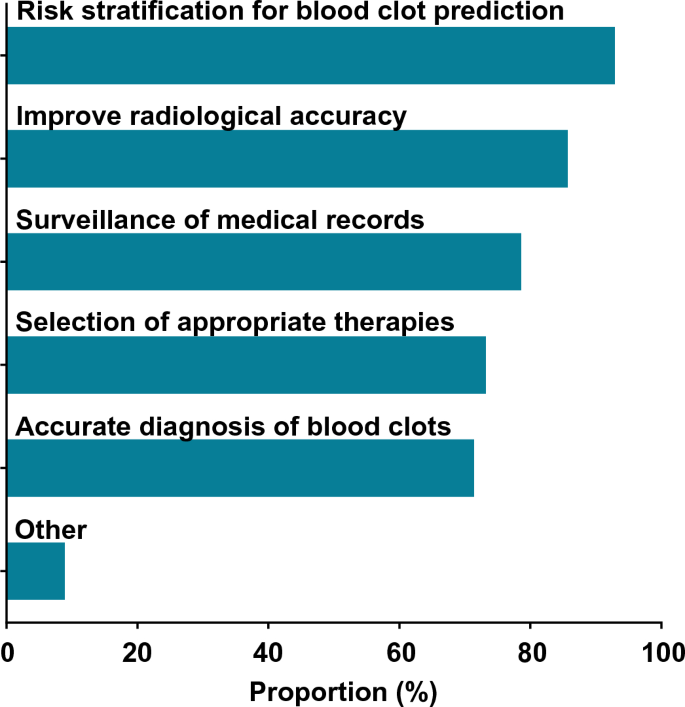
A majority of informaticians agreed that AI/ML can be utilized for medical administration of blood clots (56.0% 95% CI 46–66%). Of those 56 respondents, most agreed that AI/ML can be utilized for danger stratification (94.6%), radiologic accuracy (87.5%), surveillance (80.4%), prognosis (73.2%), and therapy (73.2%) (Fig. 2). 4 respondents proposed potential further makes use of for AI/ML: monitoring the method of clot dissolution, warfarin dosing, shared decision-making, and therapy throughout acute versus continual restoration phases. All respondents have been requested about perceived limitations, and probably the most generally cited limitations have been a scarcity of transparency with AI/ML programs (48.5%), concern that clinicians wouldn’t use an AI/ML system (34.7%), and issues round legal responsibility (24.8%) (Supplementary Desk 2). Informaticians who recognized as clinicians have been extra more likely to assume that AI may help with VTE in comparison with those that didn’t establish as clinicians, although the distinction was not statistically important (66.7% vs. 47.3%, respectively; p = 0.052). Respondents at organizations which have carried out AI weren’t considerably extra more likely to assume that AI may help with VTE in comparison with these at organizations that had not carried out AI (59.0% vs. 48.7%; p = 0.32).
All respondents have been requested the free-text query, “What else needs to be thought-about when utilizing AI/ML to help within the medical administration of blood clots?” There have been 37 responses, six of which have been faraway from evaluation as a result of they didn’t reply the questions. Of the remaining 31 responses, practically all have been associated to validation of the system and mentioned elements associated to testing, bias, and transparency. A number of responses mentioned deployment, and a couple of responses touched on the significance of clinician oversight (themes in Desk 3; coding tree in Supplementary Desk 3).