Pattern statistics
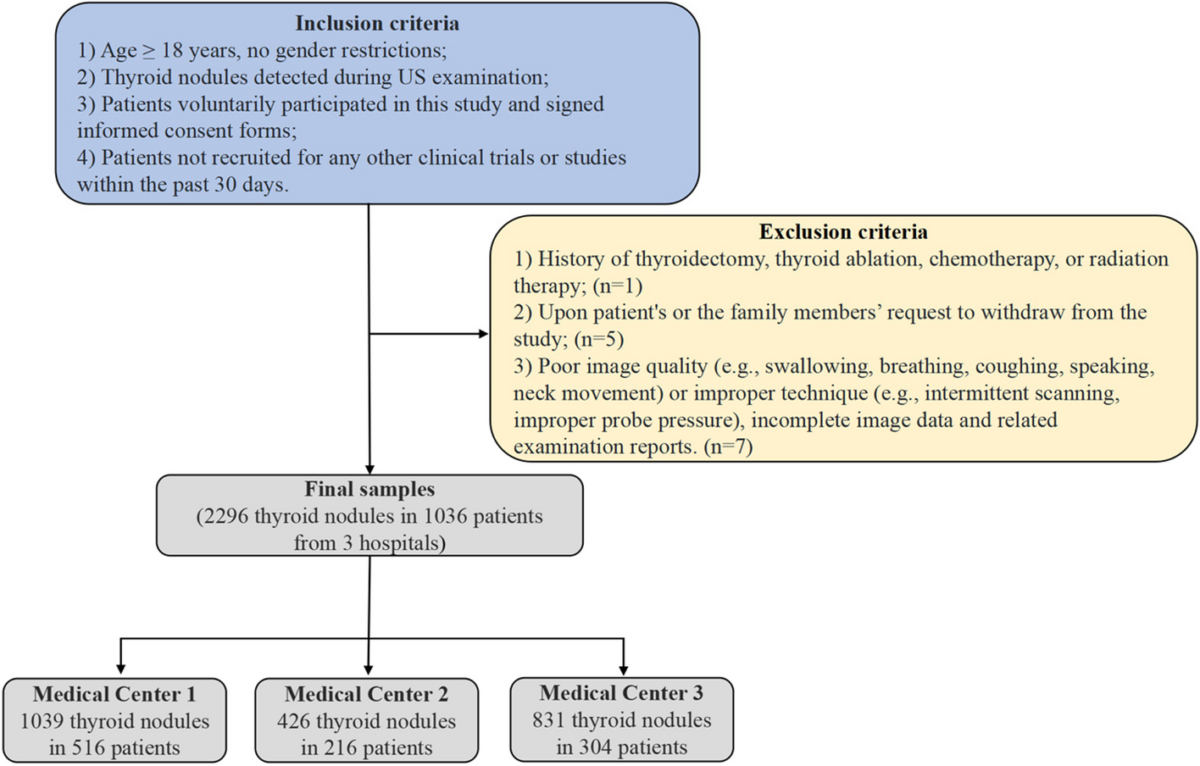
Desk 1 summarizes the essential pattern statistics of affected person age, gender, and the quantity of benign and malignant nodules decided by US examination arbitration committee, FNAC, and PPE at every medical middle. A complete of 1036 sufferers had been recruited for this study (516 sufferers from Medical Heart 1, 216 sufferers from Medical Heart 2, and 304 sufferers from Medical Heart 3), with a whole of 2296 nodules. Amongst them, there have been 260 male sufferers and 776 feminine sufferers. In keeping with the 2e diagnostic standards, a whole of 1707 nodules had been recognized as benign: amongst which 1339 nodules had been recognized by the US examination arbitration committee, 368 nodules had been recognized by pathological outcome (28 nodules had been recognized by FNAC, and 340 nodules had been recognized by PPE). There have been 589 malignant nodules, with 204 nodules recognized by the US examination arbitration committee and 385 nodules recognized by pathological outcome (11 nodules recognized by FNAC, and 374 nodules recognized by PPE).
Pathological outcome because the analysis normal
On this study, the benign and malignant nature of 753 nodules was decided by pathological outcome (amongst which 714 nodules had been decided by PPE), with 368 nodules categorized as benign and 385 nodules categorized as malignant. For these thyroid nodules, the AI system demonstrated comparable sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC to senior radiologists (0.826 vs. 0.800, 0.815 vs. 0.804, 0.821 vs. 0.802, 0.821 vs. 0.802, respectively; all p > 0.05). The specificity, accuracy, and AUC of the AI system had been superior to that of much less skilled junior radiologists (0.815 vs. 0.701, 0.821 vs. 0.745, 0.821 vs. 0.744, respectively; all p < 0.001). In comparison with impartial readings by junior radiologists, AI-assisted readings considerably improved their specificity, accuracy, and AUC (all p < 0.05). We discovered that AI-assisted junior radiologists might obtain the diagnostic stage of senior radiologists (all p > 0.05) (Desk 2).
As well as, the benign and malignant nature of 714 nodules was decided by PPE. For these thyroid nodules, the AI system demonstrated comparable efficiency to skilled radiologists in phrases of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC (all P > 0.05). The specificity, accuracy, and AUC of the AI system had been superior to these of much less skilled radiologists (all P < 0.05). The AI-assisted mode considerably improved the specificity, accuracy, and AUC of much less skilled radiologists to the extent of senior radiologists, whereas the sensitivity remained just like their impartial readings (Further file 1: Desk S2). To validate the excessive diagnostic efficiency of the US examination arbitration committee in figuring out the benign and malignant nature of thyroid nodules, sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC had been calculated utilizing PPE because the gold normal, ensuing in values of 0.789, 0.865, 0.825, and 0.827, respectively (Further file 1: Desk S2).
Analysis by the Arbitration Committee because the analysis normal
On this study, 1543 nodules had been categorized by the arbitration committee with out continuing to FNAC or PPE analysis, with 1339 nodules categorized as pro-benign and 204 nodules categorized as pro-malignant. For these thyroid nodules, the AI system demonstrated glorious settlement to senior radiologists in phrases of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC (0.946 vs. 0.941, 0.966 vs. 0.970, 0.964 vs. 0.966, 0.956 vs. 0.956, respectively; all p > 0.05). The AI system confirmed superior sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC in comparison with that of junior radiologists (all p < 0.001). In comparison with impartial readings by junior radiologists, AI-assisted readings considerably improved their specificity, accuracy, and AUC (0.875 vs. 0.955, 0.876 vs. 0.943, 0.878 vs. 0.909, respectively; all p < 0.05), however didn’t attain the extent of senior radiologists (all p < 0.05) (Desk 3).
International 2e diagnostic standards because the gold normal
Summing over all circumstances which had been analyzed individually utilizing both pathology or the arbitration committee because the diagnostic standards, or in our proposed time period, the 2e diagnostic standards, the AI system demonstrated superior sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC in comparison with junior radiologists (0.868 vs. 0.820, 0.934 vs. 0.837, 0.917 vs. 0.833, 0.901 vs. 0.829, respectively; all p < 0.001), and confirmed comparable outcomes to senior radiologists’ readings (0.868 vs. 0.849, 0.934 vs. 0.934, 0.917 vs. 0.912, 0.901 vs. 0.892, respectively; all p > 0.05). In comparison with impartial readings by junior radiologists, AI-assisted readings considerably improved their specificity, accuracy, and AUC (0.837 vs. 0.921, 0.833 vs. 0.895, 0.829 vs. 0.871, respectively; all p < 0.001), the place specificity and accuracy had been akin to these of senior radiologists (p > 0.05) (Desk 4).
As well as, the diagnostic efficiency of AI was in contrast with that of radiologists in every of the three medical facilities included in this study. In Medical Heart 1, which included 1039 thyroid nodules (Further file 1: Desk S3), the AI system exhibited greater specificity, accuracy, and AUC in comparison with junior radiologists’ readings (0.938 vs. 0.883, 0.924 vs. 0.877, 0.913 vs. 0.872 respectively; all p < 0.05), however confirmed no vital variations in comparison with senior radiologists’ readings (all p > 0.05). In comparison with impartial readings by junior radiologists, AI-assisted readings improved specificity (0.883 vs. 0.939, p < 0.001) and accuracy (0.877 vs. 0.910, p = 0.013), which had been akin to these of senior radiologists (all p > 0.05). In Medical Heart 2, which included 426 thyroid nodules (Further file 1: Desk S4), the AI system exhibited greater sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC in comparison with junior radiologists’ readings (all p < 0.05). There have been no vital variations between senior radiologists and AI in phrases of specificity, accuracy, and AUC (all p > 0.05). In comparison with impartial readings by junior radiologists, AI-assisted readings considerably improved their specificity, accuracy, and AUC (all p < 0.001), which had been akin to these of senior radiologists (all p > 0.05). There have been no vital variations in sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC between AI-assisted and impartial readings by senior radiologists (all p > 0.05). In Medical Heart 3, which included 831 thyroid nodules (Further file 1: Desk S5), the AI system exhibited considerably greater sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and AUC in comparison with junior radiologists (all p < 0.001), however comparable outcomes to skilled radiologists’ readings (all p > 0.05). Moreover, AI help led to an improved total diagnostic AUC for junior radiologists (p < 0.05).
Nonetheless, out of 2296 nodules in whole besides circumstances the place junior radiologists corrected their unique miss-classifications of nodule malignancy after consulting suggestions of the AI system (32 and 161 respective nodule circumstances for which initially miss-classified as benign or malignant had been corrected), there have been additionally circumstances the place analysis by the AI system misled the junior radiologists (17 and 14 respective nodule circumstances for which initially correctly-classified as benign or malignant had been reverted). As well as, there have been additionally circumstances the place the AI system failed concurrently because the senior radiologists (81 and 59 respective nodule circumstances the place benign and malignant nodules had been miss-classified) in response to our proposed 2e diagnostic standards(Further file 1: Desk S6). We chosen consultant thyroid nodule US photos from these circumstances proven in Fig. 3 which could present some hints in regards to the decision-makings from radiologists and the AI system.
Consultant transverse and longitudinal US photos of thyroid nodules chosen from six completely different circumstances, masking miss-diagnosis of AI and senior radiologists, success and failure in assisting junior radiologists to attain higher analysis in response to our proposed 2e analysis standards. A Each the AI system and senior radiologists recognized it as “malignant,” and the PPE was nodular goiter with adenomatous hyperplasia. B Each the AI system and senior radiologists categorized it as “benign,” but it surely was recognized to be papillary thyroid microcarcinoma in response to the PPE. C, D The AI system recognized as “malignant” and junior radiologists independently recognized as “benign,” which was nevertheless modified to “malignant” after referring to the AI. C was recognized as thyroid micropapillary carcinoma, and D as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with thyroid adenoma in response to the PPE. E, F The AI system recognized as “benign” and junior radiologists independently recognized as “malignant,” which was modified to “benign” after referring to the AI. E was recognized as papillary thyroid microcarcinoma, whereas F didn’t bear pathological examination and was thought-about as “benign” by the arbitration committee
Additionally it is attention-grabbing to judge whether or not analysis by the AI system is also useful for the junior radiologists in diagnosing isthmic nodules. That is outlined as such if the transverse US picture of the thyroid nodule is fully or largely positioned in entrance of the trachea, or in different phrases in the isthmus [25]. In contrast with the nodules in lateral lobes of the thyroid gland, nodules positioned in the isthmus might pose sure diagnostic challenges. Due to this fact, we analyzed particularly additionally nodules positioned in the isthmus of the thyroid (Further file 1: Desk S7), revealing that the AI system considerably outperformed junior radiologists in phrases of specificity and AUC (all p < 0.05) and in addition it confirmed a greater accuracy, nevertheless with out statistical distinction (p = 0.075). When in comparison with the senior radiologists, it confirmed successfully equal efficiency (all p > 0.05). In comparison with impartial readings by junior radiologists, AI-assisted readings improved specificity (0.795 vs. 0.918, p = 0.004) and AUC (0.777 vs. 0.855, p = 0.016).