AI adoption and burnout
We suggest that AI adoption in a corporation will enhance worker burnout. Adopting AI is an advanced and multi-stage course of that begins with elevating consciousness and conducting exploratory analysis and continues via large-scale implementation and ongoing refinements (Kaplan and Haenlein, 2020). A complete evaluation of a corporation’s preparedness is required, which includes , for instance, information availability, human capital, management assist, technical infrastructure, and the tradition of the firm (Berente et al. 2021; Chen et al. 2023; Magistretti et al. 2019; Makridis and Mishra, 2022; Uren and Edwards, 2023). The correct prioritization of AI use circumstances is required for organizations to attain their strategic objectives (Davenport and Ronanki, 2018). As well as, the moral, social, and governance considerations raised by AI applied sciences should be addressed in an effort to facilitate their accountable and clear deployment (Chen et al. 2023; Dwivedi et al. 2019). In an effort to absolutely make the most of AI and preserve staff engaged and well-cared-for, organizations should modify their methods, present reskilling and upskilling alternatives, and domesticate a tradition of lifelong studying (Magistretti et al. 2019; Makridis and Mishra, 2022; Uren and Edwards, 2023).
Extended interpersonal stresses in a single’s job can result in burnout, a mental situation outlined by emotional weariness, depersonalization, and a diminished sense of private success (Maslach and Leiter, 2016; Maslach et al. 2001). Depersonalization is characterised by a destructive, indifferent, and unempathetic angle towards one’s work and colleagues, whereas emotional exhaustion includes emotions of being emotionally drained and overextended (Maslach et al. 2001; Shirom and Melamed, 2006). Decreased self-confidence causes unfavorable assessments of one’s talents and, in the end, discontent with one’s life (Maslach et al. 2001; Leiter and Maslach, 2016). Burnout units in when an individual’s emotional and bodily sources are exhausted as a result of their work atmosphere is unsuitable (Leiter and Maslach, 2003). Analysis has proven that it may possibly hurt each people’ and organizations’ well-being. Some of these destructive outcomes embody issues with mental and bodily health, cognitive functioning, job satisfaction, organizational dedication, turnover intentions, productiveness, absenteeism, healthcare prices, and repair high quality (Melamed et al. 2006; Salvagioni et al. 2017; Alarcon, 2011; Lee and Ashforth, 1996; Bakker et al. 2014; Taris, 2006). Hassard et al. (2018) discovered that healthcare prices, decreased productiveness, and workers turnover contribute considerably to burnout’s substantial monetary penalties.
We argue that the adoption of AI in the office will enhance worker burnout based mostly on the JD-R mannequin, the conservation of sources (COR) principle, and the technostress mannequin (Tarafdar et al. 2007).
First, the JD-R mannequin states that job calls for and job sources are the two major classes of job traits and that they work together to affect worker well-being outcomes, together with burnout (Bakker and Demerouti, 2017). Job calls for require mental and bodily exertion from the employee, which could negatively have an effect on their health (Demerouti, Bakker, Nachreiner, and Schaufeli, 2001). AI adoption might be seen as a job demand as a result of it brings about new issues and complexities that require staff to accumulate new abilities, modify to new work processes, and collaborate with AI programs (Makridis and Mishra, 2022; Pereira et al. 2023; Uren and Edwards,2023). Moreover, employees might really feel pressured to work quicker and extra effectively if AI programs are carried out in the office (Berente et al. 2021; Chen et al. 2023), and stress and fatigue, two hallmarks of burnout, may worsen in consequence of the elevated workload (Maslach et al. 2001). Staff might also face extra psychological bills attributable to job calls for, corresponding to the must consistently study and enhance their abilities to stay related of their professions (Dwivedi et al. 2021; Zirar et al. 2023).
Second, the COR principle (Hobfoll, 1989) helps the connection between AI adoption and worker burnout. Sources comprise the issues, traits, circumstances, and vitality that a person values; based on this principle, folks work onerous to accumulate, preserve, and safeguard their sources (Hobfoll, 2001). In line with Karasek (1979) and Ryan and Deci (2000), AI can undermine staff’ sources, together with their confidence, independence, and job stability. Staff might endure from burnout in the event that they really feel emotionally and mentally drained from worrying about shedding these sources in consequence of AI implementation (Hobfoll, 2001).
Third, the technostress mannequin (Tarafdar et al. 2007) additional clarifies the affiliation between expertise adoption and worker well-being. Technostress is the stress skilled by people attributable to the use of info and communication applied sciences (ICTs) in the office (Tarafdar et al. 2019). The adoption of AI applied sciences might be considered as a selected occasion of ICT implementation; thus, the technostress framework might be utilized to grasp AI’s affect on worker burnout. Tarafdar et al. (2007) recognized 5 key technostress creators: techno-overload, techno-invasion, techno-complexity, techno-insecurity, and techno-uncertainty. These technostress creators can manifest throughout AI adoption, resulting in elevated stress and burnout amongst staff (Khedhaouria and Cucchi, 2019). Particularly, techno-overload happens when AI applied sciences enhance workload and speed up work tempo, compelling staff to work extra intensively (Borle et al. 2021). Techno-invasion refers to the erosion of the boundaries between one’s work and private life attributable to fixed connectivity and availability expectations related to AI programs (Tarafdar et al. 2007). Techno-complexity arises when staff discover AI applied sciences obscure and use, inflicting emotions of inadequacy and frustration (Tarafdar et al. 2011). Techno-insecurity is the worry of job loss or displacement attributable to AI, whereas techno-uncertainty denotes the continuous modifications and upgrades in AI applied sciences that require staff to adapt and purchase new abilities recurrently (Khedhaouria and Cucchi, 2019). In mild of these arguments, the following speculation is proposed.
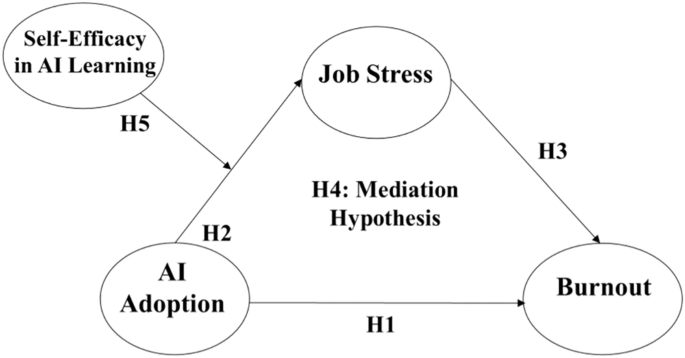
Speculation 1: AI adoption in a corporation will enhance burnout.
AI adoption and job stress
This paper means that AI adoption in a corporation will enhance job stress amongst staff. Job stress is a fancy idea that encompasses the mental, emotional, and bodily responses that employees show when confronted with challenges at work which can be too troublesome for them to deal with (Lazarus and Folkman, 1984). When folks face substantial strain, difficulties, and calls for at work, it may possibly result in destructive bodily reactions in addition to psychological pressure (Ganster and Rosen, 2013).
We suggest that the adoption of AI in a corporation will enhance job stress amongst staff by drawing on the JD-C) mannequin (Karasek, 1979) and the particular person–atmosphere (P–E) match principle (Edwards et al. 1998).
First, based on the JDC mannequin, job stress is brought on by the interplay between job calls for and job management. Workload, time constraints, and role conflicts are all examples of psychological stressors that staff face on the job (Karasek and Theorell, 1990). Conversely, job management is outlined as the diploma to which employees can train company and competence of their work (Karasek, 1979). Excessive job calls for, coupled with a scarcity of management over these calls for, enhance job-related stress, based on the JD-C mannequin (Häusser et al. 2010). One interpretation of AI’s widespread use in a corporation is that it’ll enhance the calls for imposed on human employees. When AI applied sciences are carried out, personnel are usually required to study new abilities, modify to totally different work processes, and work with AI programs (Pereira et al. 2023; Zirar et al. 2023). As employees attempt to adapt to the new calls for imposed by AI, they could discover themselves underneath stricter effort and time constraints (Bankins et al. 2024; Pereira et al. 2023). Role ambiguity and battle might also come up from AI programs’ complexity and opaqueness as employees attempt to make sense of their evolving duties in relation to AI (Bankins et al. 2024; Pereira et al. 2023).
At the identical time, AI adoption may make employees really feel that they’ve much less management over their jobs. As AI programs take over duties and decision-making roles beforehand carried out by people, staff may expertise a discount in autonomy and decision-making energy (Budhwar et al. 2022). The opaque nature of many AI algorithms can additional erode staff’ sense of management, as they could discover it difficult to grasp and affect the outcomes generated by these programs (Shrestha et al. 2021). Moreover, when AI is carried out in the office, people might expertise heightened job stress in keeping with the JD-C mannequin’s description of increased job expectations and decrease job management.
Secondly, the P–E match principle helps the concept that AI adoption can enhance stress in the office. On this view, stress develops every time a person’s abilities, wants, and values, for instance, don’t align with what’s required or offered by their office (Edwards et al. 1998). The widespread use of AI can result in a abilities hole between employees’ current talents and the talents required by the expertise (Makarius et al. 2020). A abilities hole may emerge, including to worker stress, as AI programs are all the time evolving and requiring steady studying and adaptation (Nam, 2019). One other concern with AI adoption is that it may possibly make employees really feel much less empowered than they really are (Pereira et al. 2023). Staff might really feel powerless as a result of their need for management conflicts with the actuality of their work atmosphere, particularly as AI takes over decision-making and limits staff’ discretion. In line with the P–E match principle, this misalignment can intensify job stress (Edwards et al. 1998).
Thirdly, the socio-technical programs principle (Trist and Bamforth, 1951) highlights the hyperlink between AI adoption and job stress. This principle emphasizes that a corporation’s social and technological subsystems should be aligned to enhance worker efficiency and well-being (Baxter and Sommerville, 2011). A brand new set of instruments, strategies of operation, and standards for making selections are created by the introduction of AI (Vrontis et al. 2022). Staff might discover that their wants battle with these of the AI-enhanced office if the social subsystem—which includes parts like job tasks, talents, and interpersonal relationships—isn’t correctly adjusted to the new technical subsystem (Pereira et al. 2023; Zirar et al. 2023). As a result of of this misalignment, employees might expertise extra job stress as they attempt to adapt to their new positions, study mandatory abilities, and cope with the social results of AI adoption (Shrestha et al. 2021).
Speculation 2: AI adoption in a corporation will enhance job stress.
Job stress and worker burnout
We argue that job stress will enhance burnout amongst staff based mostly on the COR principle (Hobfoll, 1989), the transactional mannequin of stress and coping (TMSC; Lazarus and Folkman, 1984), and the JD-R mannequin (Demerouti et al. 2001).
To start, based on the COR principle, folks work onerous to accumulate, preserve, defend, and domesticate sources that they worth. Issues, qualities, circumstances, or energies that a person values or that assist them purchase extra vital sources are examples of sources (Hobfoll et al. 2018). People expertise stress when they’re in danger of shedding sources, really lose sources, or fail to accumulate sources after making substantial investments (Hobfoll, 2001). Office stress might be considered as a situation of diminished sources. In line with Bakker and Demerouti (2017), employees expertise excessive ranges of office stress as a result of they’re being requested to do extra with much less. Emotional and bodily tiredness, in addition to mental stress, could also be indicators of useful resource depletion (Alarcon, 2011). Burnout can develop after a protracted interval of work underneath traumatic circumstances and useful resource shortage (Hobfoll et al. 2018).
Second, based on the TMSC, folks expertise stress once they really feel like they lack the coping sources mandatory to satisfy the calls for of a state of affairs. This means that cognitive appraisal and coping mechanisms are integral elements of the transactional course of via which a person experiences stress (Lazarus, 1999). Office stress is extra frequent amongst employees who imagine their workload exceeds their skill to manage in comparison with those that don’t maintain this perception (Goh et al. 2015). The important part of burnout is the bodily, emotional, and mental depletion created by extended publicity to job stress (Maslach et al. 2001). In line with the TMSC, burnout can happen when employees’ emotional and cognitive sources are depleted attributable to an incapability to deal with job pressures (Guthier et al. 2020). That is in keeping with the COR principle’s supposition that depletion and loss of sources result in burnout (Hobbow et al. 2018).
Third, the JD-R mannequin reveals how stress at work can result in burnout. Job calls for and job sources are the two major branches of job traits (Demerouti et al. 2001). Job calls for comprise the social, organizational, and bodily demanding elements of a job that trigger one to incur physiological and psychological bills over time (Bakker and Demerouti, 2007). Excessive ranges of emotional and mental pressure, in addition to time constraints, are examples of calls for in the office (Bakker et al. 2014). In the meantime, job sources are the bodily, mental, social, and organizational elements of a job that assist employees accomplish their objectives, address stress, and develop themselves professionally and personally (Bakker and Demerouti, 2007). Social assist, autonomy, and efficiency analysis are examples of job sources (Van der Heijden et al. 2019). Employee pressure and burnout are each predicted by the JD-R mannequin, which states that employees usually tend to expertise the former when job calls for are excessive and job sources are low (Demerouti et al. 2001). Burnout is characterised by emotional, mental, and bodily tiredness; it may be brought on by job stress, which happens when calls for are excessive and sources are scarce (Maslach et al. 2001).
Speculation 3: Job stress will enhance burnout.
The mediating role of job stress in the relationship between AI adoption and burnout
Analyzing how work stress mediates the affiliation between AI adoption in a corporation and burnout is one of the major objectives of this examine. By combining the JD-R mannequin, the COR principle, and the TMSC, we anticipate job stress to operate as a mediator in the AI adoption-burnout hyperlink.
First, worker well-being and organizational outcomes are affected by the interaction between job calls for and job sources, that are labeled based on the JD-R mannequin (Bakker and Demerouti, 2017). AI adoption in a corporation will create a necessity for extra folks to study and adapt to new expertise, extra work to perform, and probably extra role ambiguity (Bankins et al. 2024; Pereira et al. 2023). The JD-R mannequin postulates that burnout and different destructive results might happen when work calls for exceed out there sources.
Secondly, based on the COR principle, stress on the job mediates the hyperlink between AI adoption and burnout. In line with this principle, folks work onerous to get what they need and preserve what they’ve (Hobfoll et al. 2018). Staff’ confidence, independence, and job stability are amongst the sources that may be jeopardized by the introduction of AI. Staff might endure from emotional and mental exhaustion and burnout in the event that they fear that AI integration will value them their sources (Hobfoll, 2001).
Lastly, the operate of job stress as a mediator between AI adoption and burnout is additional defined by the TMSC. This paradigm proposes that when folks face a problem, like adopting AI, they perform a cognitive appraisal to find out how critical the problem is and what sources they possess for coping with it (Lazarus and Folkman, 1984). Staff might really feel extra strain at work in the event that they fear that AI adoption might undermine their job stability, work identification, or skill to execute their jobs effectively and if they don’t suppose they will cope with these points. Staff might endure from burnout in the event that they consistently expertise a stage of stress that they can not deal with.
In mild of the arguments outlined above, we offer the following speculation.
Speculation 4: Job stress will mediate the affiliation between AI adoption in a corporation and burnout.
The moderating affect of self-efficacy in AI studying on the hyperlink between AI adoption and job stress
We hypothesize that the growing impact of AI adoption on work stress will likely be weakened by a person’s confidence of their AI studying capabilities. On this context, self-efficacy in AI studying is an individual’s confidence of their skill to find out about and work with AI (Bandura, 1977). Extra particularly, this context-specific assemble signifies how assured an individual is of their skill to work together with AI programs, perceive AI concepts, and successfully use AI instruments (Kim and Kim, 2024). The idea of self-efficacy in AI studying originates from Bandura’s SCT (Bandura, 1986). This principle posits that how somebody perceives their skills impacts their motivation, actions, and achievement in a sure space. One’s perceptions of their skill to study AI can affect how a lot effort and time persons are ready to dedicate to AI-related duties, how effectively they deal with setbacks, and the way successfully they observe what they’ve discovered (Kim and Kim, 2024).
The hyperlink between AI adoption and worker job stress might be higher understood by delving into the moderating impact of worker self-efficacy in AI studying. Based mostly on the TMSC and SCT, we suggest that the impact of the adoption of AI on job stress will likely be weakened if staff place confidence in their capability to grasp and make the most of the expertise.
First, the SCT proposes that a person’s self-efficacy—their confidence of their talents to hold out the actions that can result in a desired consequence—strongly influences their reasoning, drive, and feelings (Bandura, 1997). The time period “self-efficacy in AI studying” is utilized in the context of AI adoption to explain an worker’s perception of their capability to accumulate and use information and abilities pertaining to AI (Bandura, 1986). People with increased self-efficacy are much less careworn, extra inclined to understand setbacks as studying experiences, and extra prepared to persevere in the face of adversity (Bandura, 1997). Moreover, the TMSC sheds mild on how self-efficacy elements into stress analysis (Lazarus and Folkman, 1984). In line with this mannequin, folks carry out a cognitive evaluation when confronted with a attainable stressor, corresponding to the implementation of AI at work, to find out the gravity of the scenario and the way effectively they will cope (Lazarus and Folkman, 1987). Regarding AI, staff who place confidence in their talents to study and adapt to new applied sciences are prone to view AI adoption as a process they will accomplish moderately than an amazing hazard.
Staff who’ve excessive ranges of self-efficacy in AI studying additionally place confidence in their talents to study and use AI effectively (Bandura, 1997). In line with SCT, this group is extra prone to see the widespread use of AI as an opportunity for skilled and private improvement moderately than a hazard (Bandura, 2012). These employees are all the time searching for new methods to enhance their information and skills and are fast to undertake new expertise (Chae et al. 2019). The calls for of AI adoption might be higher managed by employees who imagine of their functionality to study AI than those that don’t maintain this perception.
Moreover, the TMSC (Lazarus and Folkman, 1987) means that these people can understand the adoption of AI as a manageable stressor throughout the major evaluation course of since they’re assured of their skill to accumulate the important talents wanted to work with AI. Their coping sources, together with their AI studying capacities, are prone to be deemed applicable throughout the secondary analysis course of to satisfy the calls for of the scenario. Staff who place confidence in their talents to study AI are comparatively unlikely to really feel threatened by the adoption of AI in the office. It is because they’re assured of their skill to adapt and revenue from the course of.
For instance, if a corporation makes use of AI to energy its CRM programs, employees with excessive self-efficacy in AI studying may view the scenario as an opportunity to hone their customer support abilities whereas additionally successfully utilizing the information AI gives to craft distinctive encounters for every consumer. These employees can even be extra inclined to participate in coaching packages, ask for assist once they want it, and check out utilizing new CRM applied sciences in an effort to attain their full potential. Furthermore, they will adapt to new expertise with much less stress than different employees since they actively hunt down sources to develop their AI competencies and interact in proactive studying actions. In consequence, they don’t fear excessively about failing to satisfy expectations and are assured of their skill to make use of an AI-powered CRM system to enhance their firm’s efficiency.
This example is reversed when employees lack self-efficacy of their talents to grasp and make the most of AI-related info (Bandura, 1997). SCT claims that these persons are extra liable to view AI adoption as a menace to their job safety and competence, owing to their heightened nervousness and rigidity (Bandura, 2012). They could act in ways in which forestall them from studying, resist studying alternatives, and have hassle adjusting to new applied sciences (Charness and Boot, 2016). As well as, employees who don’t imagine of their talents to study AI may wrestle to satisfy the challenges of AI implementation. In consequence, when an organization implements AI programs, these employees are prone to really feel careworn as a result of they aren’t ready to cope with the new tasks and obstacles that can inevitably come up.
That is supported by the TMSC’s suggestion that staff who lack confidence of their skill to accumulate AI are prone to view AI adoption as a traumatic occasion that they can not handle throughout the main evaluation course of (Lazarus and Folkman, 1987). They might conclude that their coping sources, particularly their AI studying capabilities, are insufficient to deal with the scenario’s calls for throughout the secondary appraisal course of. People who lack confidence of their skill to study AI face elevated office stress, difficulties adjusting to their organizations’ AI adoption practices, and uncertainty concerning their future with the firm (Bankins et al. 2024; Pereira et al. 2023).
As an illustration, staff who don’t suppose they’re good at studying learn how to use AI may really feel intimidated by the new CRM instruments that a corporation installs. They might be immune to coaching classes, hesitant to make use of new buyer relationship administration programs, and apprehensive about shedding their jobs to AI (Meyer and Hünefeld, 2018). In consequence, these employees will really feel elevated stress on the job as they fear about failing to attain the new requirements set by the AI-powered CRM system and their incapability to regulate to it.
The following speculation relies on the above theoretical concerns:
Speculation 5: Self-efficacy in AI studying will average the hyperlink between AI adoption in a corporation and job stress such that the constructive affiliation between AI adoption and job stress will likely be weaker for workers with excessive self-efficacy in AI studying in comparison with these with low self-efficacy.
Determine 1 illustrates the conceptual mannequin utilized on this examine, which depicts the hypothesized relationships between AI adoption, job stress, and burnout, in addition to the moderating role of self-efficacy in AI studying.